Showing 802–810 of 1403 resultsSorted by latest
-

WWII German Latvian Propaganda – Both Versions – Rare
The Ladies in the background are representing Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. Two versions of the same flyer, in both languages. Not seen another of this type, in roughly A4 Size
-

WW1 German Soldbuch and Militärpass – Iron Cross Cert – Musketier Ernst Hasenauer – Reserve Infanterie Regiment Nr 222 – Richtschütze MG08/15 (Sold)
Nice set to Musketier Ernst Hasenauer Reserve Infanterie Regiment Nr 222 Iron Cross – 14.10.1918 – Hermann Stellung Bravery Medal – 25.11.1917 Trained on MG08/15 as a gunner. Iron Cross Cert – 48 Reserve Division The 48th Reserve Division initially fought on the Western Front, entering the line in October between the Meuse and Moselle. It then moved to the Flanders and Artois regions in the drive northwards known as the Race to the Sea. It fought at Lille in late October and at Ypres into November. At the end of November, the division was transferred to the Eastern Front. It fought in a number of engagements, including the winter 1914 Battle of Łódź, and then participated in the pursuit of the Russians from Carpathia and Austrian Galicia known as the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive after the major battle at Gorlice and Tarnów. The division remained in positional warfare and various engagements on the Eastern Front thereafter, and faced part of the Brusilov Offensive in 1916. From October 1916 to April 1917, the division was attached to the Austro-Hungarian 3rd Army, and was then attached to the Austro-Hungarian 2nd Army. In May 1917, the division returned to the Western Front, and occupied the line near Verdun, facing the French offensive there in August and September. The division was in the trenches in Lorraine from the end of September to the beginning of December 1917, and then in Upper Alsace until mid-February 1918. It then went into army reserve until April, when it went into the line in the Flanders and Artois regions. It remained in the fighting in the northern part of the Western Front until the end of the war. In 1917, Allied intelligence rated the division as a mediocre division. In 1918 it was rated second class.
-

WWI German Soldbuch / Wehrpass WWII – Photos – Uffz Ledermann – 15 Landwehr Division – Fort Vaux – Crimea Ukraine – Iron Cross – Wounds Badge (Sold)
Eduard Ledermann Lived in Russian Czarist Empire – issued a Czarist ID Booklet. Incredible: Piotrków Governorate (Russian: Петроковская губерния; Polish: Gubernia piotrkowska) was one of the administrative divisions (guberniya; gubernia) in the Kingdom of Poland, established in 1867 by splitting some areas of the Radom and Warsaw Governorates. Its capital was in Petrokov (Russian: Петроко́в) in modern day Piotrków Trybunalski. Joined Landwehr Infanterie Regiment 53 – 15 Landwehr Division Iron Cross and Wounded by grenade splinters in Verdun 1916. Nice photos of Ledermann in uniform in WW1. The association was originally assembled as the Borries Division on January 9, 1915 on the Western Front and was statised on July 13, 1915 as the 15th Landwehr Division. She fought in the west until mid-March 1917 and was then transferred to the eastern front. After the armistice there, the division took part in the fighting in support of the Ukraine and did not return home until mid-March 1919 after the end of the war. Der Verband wurde ursprünglich als Division Borries am 9. Januar 1915 an der Westfront zusammengestellt und am 13. Juli 1915 als 15. Landwehr-Division etatisiert. Bis Mitte März 1917 kämpfte sie im Westen und wurde dann an die Ostfront verlegt. Nach dem dortigen Waffenstillstand war die Division an den Kämpfen zur Unterstützung der Ukraine beteiligt und kehrte nach Kriegsende erst bis Mitte März 1919 in die Heimat zurück. 1915 9. Januar bis 16. Oktober — Stellungskämpfe westlich Roye-Noyon ab 21. Oktober — Stellungskämpfe westlich Roye-Noyon 1916 Stellungskämpfe westlich Roye-Noyon 28. Januar bis 17. Februar — Kämpfe von Frise 1917 bis 15. März — Stellungskämpfe westlich Roye-Noyon 16. bis 19. März — Kämpfe vor der Siegfriedfront 20. bis 31. März — Transport nach dem Osten 1. April bis 7. Dezember — Stellungskrieg westlich Brody 7. bis 17. Dezember — Waffenruhe ab 17. Dezember — Waffenstillstand 1918 bis 18. Februar — Waffenstillstand 18. Februar bis 21. Juni — Kämpfe zur Unterstützung der Ukraine 16. bis 20. März — Gefechte bei Snawjonka 18. März — Gefecht bei Nowo-Ukrainka 31. März bis 6. April — Gefechte bei Kriwoj-Rog 24. bis 25. April — Gefecht bei Kolaj 30. April bis 1. Mai — Einnahme von Sewastopol 22. Juni. bis 15. November — Besetzung der Ukraine ab 16. November — Räumung der Ukraine 1919 bis 16. März — Räumung der Ukraine
-

WWI German Soldbuch & Militärpass – Uffz Josef Bläser – Infanterie Regiment Nr 25 -Wounded in Lodz Poland – Somme – Iron Cross (Sold)
A nice set with photos to Bläser, Fighting with the following units: Inf Reg Nr 25 – 1914 – Wounded in Lodz, Poland 1916 – Inf Reg No 68, 1917 , Inf Reg 161 – Fighting on the Western Front, Somme and Ypren. Promoted to NCO, awarded the Iron Cross 1917 Photos: Small Portrait, 7 x larger photos. Really nice set here, not often seen like this anymore.
-

WW1 German Soldbuch and Feldpost – Musketier Wiese – Reserve Infanterie Regiment Nr 205 – Iron Cross – Passchendaele 1917 Verdun (Sold)
Soldbuch issued to Wilhelm Wiese, born in 1896 in Prussia. Joined the Army in 1915. 15 x Feldpost matching – wrote from all over, I see stamps from Belgium also. Iron Cross in Verdun 1917 Reserve Infanterie Regiment Nr 205 44 Reserve Division The 44th Reserve Division initially fought on the Western Front, fighting on the Yser in October–November 1914 and storming Diksmuide in mid-November. It remained in positional warfare along the Yser until June 1915, and fought around Ypres in April–May. In June, it was transferred to the Eastern Front. It fought in the Gorlice-Tarnów Offensive, including the 1915 Battle of Lemberg and the assault on Brest-Litovsk. It then participated in the Serbian Campaign. After the campaign, it remained in reserve until returning to the Western Front in February 1916. It then fought in the Battle of Verdun. In July 1916 the division fought in the Battle of the Somme and then occupied various parts of the trenchline. In April 1917, it fought in the Second Battle of the Aisne, also known as the Third Battle of Champagne (and to the Germans as the Double Battle on the Aisne and in the Champagne). Thereafter, the division went into the trenchline around Verdun, remaining there until October 1917, when it joined the Battle of Passchendaele. The division then remained in the line mainly around Flanders until September 1917, when it went to Lorraine. It ended the war at the Germans’ Antwerp/Meuse position. In 1918, Allied intelligence rated the division as first class, although in 1917 it had noted shortcomings in the division’s performance as an assault division.
-

WW1 German Soldbuch and Militärpass – Führerschein with Photo – Pass for the Saar – Uffz Gerwert – Iron Cross – Wounds Badge – 237 Infanterie Division (Offer Accepted)
Nice set with photo of Karl Gerwert from the Saar Area. Soldbuch – Complete full with entries Militärpass – Seems he fought with the Infanterie Regiment 60, IR 166, and by 1918 he was in a Flak Schweinwerfer unit. Fought in the Eastern Front, won the Iron Cross Second Class and was wounded, awarded the Wounds Badge in Black. Souvenir from a Czarist Soldier – took a letter from a Czarist Soldier. Wrote in 1917, a sad letter from a wife to the soldier Nikolai, Ivanovich Saltsov. Come home, she had to sell the pig, parcel is missing. Nice drivers licence so we can see how he looked.
-
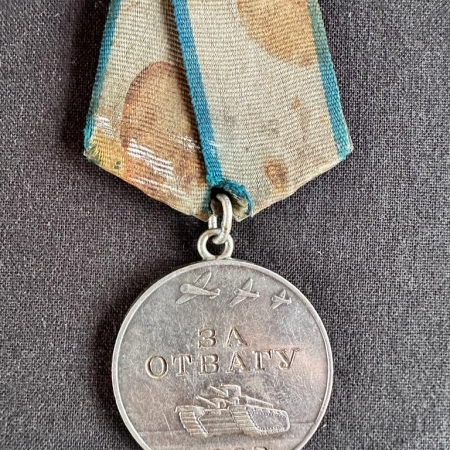

WWII Soviet Medal for Courage – ЗА ОТВАГУ – With Archive Research – 241st Rifle Division – Other medals
Korzhenko Alexey Ivanovich Date of Birth: 1921 Place of call: Teplik RVC, Ukrainian SSR, Vinnitsa region, Teplic district Date of call: 1940 Military rank: red army soldier Military unit: 1010th artillery regiment of the 241st rifle division Awards: Medal “For Courage” Order of the Red Star Order of the Patriotic War, 1st class Awarded for: The driver of the howitzer of the 6th battery of the Red Army soldier Alexei Korzhenko, for the fact that he repeatedly brought ammunition to direct point under enemy fire, the car was damaged twice by an enemy shell, but Korzhenko, despite the enemy fire, restored the car.
-
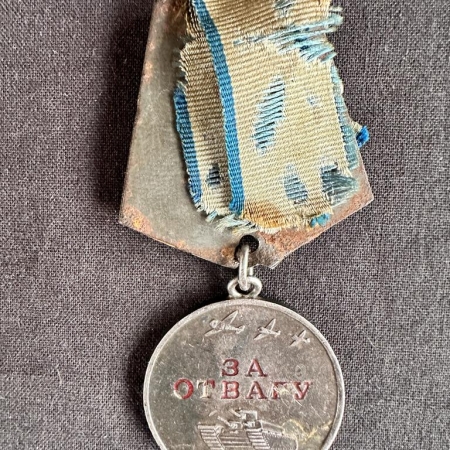
WWII Soviet Medal for Courage – ЗА ОТВАГУ – With Archive Research – 6 Airborne Division – Jassy – Bratislava 1945 – Ukrainian
Fuzhenko Mikhail Filippovich Born: 1925 Private. Position, unit: pontoner – driver of the 35th Separate Personnel Pontoon-Bridge Battalion (TMP). Participation in combat operations to defend the USSR and the Patriotic War (where, when): from 06.44 to 08.44, 2 UV, 2 Separate anti-tank brigade 1323 IPTAP and 01.45 and to 04.45, 2 UV, 6 airborne division, 20 Guards. airborne regiment. Injuries (where, when): Slightly wounded on 08/26/1944 and 04/05/1945 – a blind shrapnel wound of the soft tissues of the left leg. Since what year in the Red Army: since March 1, 1944. By what military commissariat he was called: Krivoozersky, Odessa region. Summary of personal combat exploits or merit: Fuzhenko, an active participant in the Great Patriotic War since June 1944 in the position of a loading gun of the 1323th anti-tank artillery regiment, 2 separate anti-tank artillery brigade, was slightly wounded – a blind shrapnel wound to the left shoulder blade, near the city of Jassy, Romania. He was wounded for the second time near the city of Bratislava on April 5, 1945 – a slight blind shrapnel wound to the lower third of the left lower leg. The injuries did not interfere with a good work. Fuzhenko, as part of the gun crew, actively participated in the battles for the capture of the city of Jassy, Romania. Participated in the crossing of the rivers Gron, Vag. As an active participant in the Patriotic War, he deserves to be awarded the medal “For Courage”.
-

WW1 German Militärpass Grouping – Machine Gunner MG08 – Landwehrman Friederich Zeller – Landwehr Infanterie Regiment Nr 6 – West and Eastern Front
Landwehrman Friederich Zeller born in 1896 in Baden, germany. Joined in September 1916 – Grenadier Regiment 109 – then arrived at frontline unit. Military Pass Book / Service Record – Landwehr Infanterie Regiment Nr 6 (3 Landwehr Division) – 10.1916 till 3.1917 – Trained on MG08 in July 1918 – Battle calendar: The division was put together on the Eastern Front with the mobilization on August 2, 1914 and was deployed here until September 1918. Then, in the final months of the war, she was transferred to the Western Front. After the armistice, the association returned home, where it was demobilized and finally dissolved in January 1919. 1914 August 24 – Battle of Nowe-Miasto August 27 – Battle of Gielniow August 29 – Battle of Nowo-Radomsk September 4 – Battle of Lipa-Niklas September 5 – Battle of Ciszyca-Gorna September 7-9 – Battle of Tarnavka September 17-18 – Battle of Wola-Ranizowska October 4-5 – Battles of Opatov and Radom October 9-20 – Battle of Ivangorod October 21-24 – Battles of Pilica 22 1915 to 28 October – battles on the Rawka 5 November to 15 December – battles near Czenstochowa 18 December – battles near Krasocin from 19 December – battles on the Lososina and Czarna 1915 to 12 May – battles on the Lososina and Czarna May 13th – battles at Tumlin and Kuzniaki May 14th – battles at Suchedniow May 16th – battles at Mirzec and Wierzbica May 17th – battles at Osiny May 18th – July 16th – trench warfare at Ilza July 17th – breakthrough battle at Sienno July 18-19 – Battles on the Ilzanka July 20-21 – Breakthrough of the idea of Ivangorod east of Zvolen July 22-28 – Reconnaissance battles on the Vistula July 29 – Vistula crossing July 30-August 7 – Battles on the east bank of the Vistula around Maziejowice August 8-18 – Pursuit battles between the Vistula and Bug August 19-24 – Battle of the Pulwa-Nurzec August 25-31 – Pursuit battles on the Bialowieska-Puszcza August 1-12 September – Battles on the Jasiolda and on the Zelvianka September 13-18 – Battle of Slonim September 19-24 – Battles on the upper Shchara-Servech from September 25 – Position battles on the upper Shchara-Servech 1916 Position battles Upper Shchara-Servech July 3 – 29 – Battle of Baranovichi 1917 – December 14 – Trench battles on the upper Shchara-Servech December 15 – 17 – Armistice from December 17 – Armistice 1918 – February 18 – Armistice 18 February to March 21 – fights in support of Ukraine March 22 to September 21 – occupation of Greater Russia September 27 to 30 – fighting on the Siegfried Front October 1 to 17 – defensive battle in Flanders October 18 to 24 – Rearguard fighting between Yser and Lys October 25th to November 1st – Battle of the Lys November 2nd to 4th – Rearguard fighting on both sides of the Scheldt November 5th to 11th – Retreat fighting in front of the Antwerp-Maas position from November 12th – Evacuation of the occupied territory and march home. 2. Battle Calendar – 1916 till 1919 – Russian Front, Western Front 3. WW2 1943 – Wehrmacht Ausmusterungsschein – Not mustered – with photograph of Zeller. 4. WW2 Heer Wehrpass – WW1 Service entered only. A nice grouping, WW1 service on both fronts, and was a MG08 Gunner, this is not easy found anymore especially with photos of the soldier.




